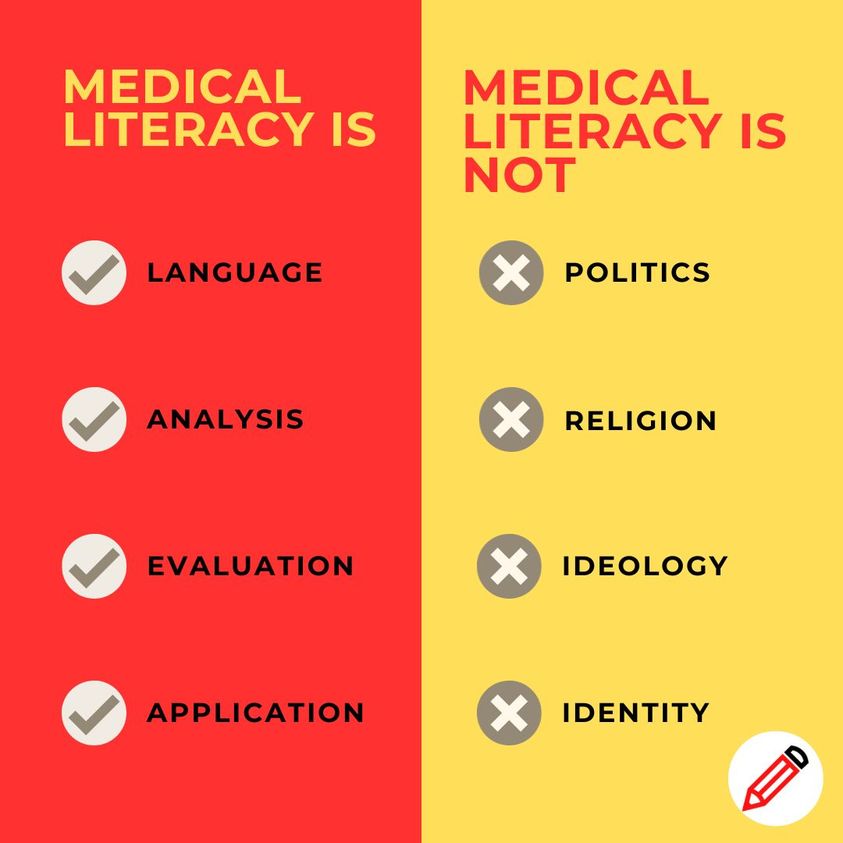
In the ever-evolving landscape of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education, the integration of medical literacy skills fosters a generation of scientifically literate individuals adept at navigating complex healthcare landscapes. Rooted in the principles of language, analysis, evaluation, and application, medical literacy transcends political, religious, ideological, and identity boundaries, offering a pathway to informed decision-making, critical thinking, and innovation within the realm of STEM.
The Foundation of Language
At the heart of medical literacy lies the mastery of language—a nuanced understanding of medical terminology, scientific concepts, and healthcare discourse. In the context of STEM education, language serves as the gateway to comprehension, enabling students to decipher complex medical texts, communicate effectively with peers and professionals, and articulate their ideas with clarity and precision. From anatomical terminology to biochemical pathways, language forms the bedrock upon which medical literacy skills flourish, empowering students to engage meaningfully with healthcare knowledge and discourse.
The Art of Analysis
Analysis, the cornerstone of scientific inquiry, forms an integral component of medical literacy within STEM education. Through analysis, students dissect medical literature, interpret research findings, and discern underlying patterns and trends. They scrutinize case studies, clinical trials, and epidemiological data, honing their analytical skills to extract valuable insights and draw evidence-based conclusions. Analysis transcends mere data interpretation—it cultivates a mindset of curiosity, skepticism, and inquiry, empowering students to question assumptions, challenge conventions, and explore new frontiers in healthcare research and innovation.
The Power of Evaluation
In the pursuit of medical literacy, evaluation guides students in discerning the reliability, validity, and relevance of healthcare information. In an era inundated with health-related content—from online forums to social media platforms—students must navigate a landscape fraught with misinformation, bias, and conflicting perspectives. Through rigorous evaluation, they learn to critically appraise sources, assess research methodologies, and differentiate between evidence- or experience-based insights and unsubstantiated claims. Evaluation equips students with the discernment to navigate the complexities of healthcare information, empowering them to make informed decisions and advocate for sound practices within STEM fields.
The Application of Knowledge
Ultimately, the essence of medical literacy transcends theoretical understanding—it resides in the practical application of knowledge to real-world contexts. In STEM education, students engage in hands-on experiences, simulations, and problem-solving exercises, applying medical concepts to clinical scenarios, research projects, and healthcare innovations. They collaborate with peers, engage with healthcare professionals, and immerse themselves in experiential learning opportunities, bridging the gap between theory and practice. Through application, students cultivate the skills, competencies, and confidence to address healthcare challenges, drive innovation, and effect positive change within their communities and beyond.
Beyond Politics, Religion, Ideology, and Identity
It is imperative to underscore that medical literacy in STEM education transcends political, religious, ideological, and identity considerations. At its core, medical literacy is rooted in scientific inquiry, empirical evidence, and ethical practice—it is a testament to the power of knowledge, curiosity, and critical thinking. In an increasingly polarized world, where healthcare decisions are often entangled with political agendas, cultural beliefs, and social identities, fostering a culture of impartiality, objectivity, and empirical reasoning is paramount.
Medical literacy in STEM education is not about espousing specific political viewpoints, religious doctrines, ideological stances, or identity affiliations—it is about equipping students with the tools, skills, and mindset to navigate the complexities of healthcare knowledge and discourse with integrity, empathy, and humility. It is about fostering a community of lifelong learners committed to the pursuit of truth, and the promotion of human well-being.
In conclusion, medical literacy in STEM education embodies the spirit of intellectual curiosity, critical inquiry, and ethical practice. Grounded in language, analysis, evaluation, and application, medical literacy empowers students to navigate the intricate landscapes of healthcare with discernment, compassion, and integrity.
===
Interested in teaching medical literacy pain free? Shop medical literacy resources!

This article was drafted by ChatGPT and edited by Joan Lee Tu, the founder of MedULingo.com.
You may also be interested in the following articles:
Why Medical Literacy Needs To Be In Your School STEM Program
Why a Robust STEM Education Program Needs to Include Medical Literacy
20 Benefits of Including Medical Literacy in Your STEM Program
How Medical Literacy Activity Books Empower Learners in STEM Education
How to Empower Future STEM Innovators with Self-Directed Learning in Medical Literacy
Why STEM Education Needs Medical Literacy to Foster Healthcare Innovators
Why You Need Diverse Learning Modalities for Medical Literacy
Building Foundational Medical Literacy Skills in STEM Education
Four Cs of Medical Literacy: Comprehension, Conversation, Communication, Collaboration

